Candlelighters has funded research into the understanding and treatment of childhood cancers for 30 years. Academic neurosurgeon, Ryan Mathew, has been supported by Candlelighters since 2018, as part of a four year funding programme to enhance brain tumour research.
Ryan qualified as a doctor in 2005 from the University of Leeds. Following hispassions of neurosurgery and research, he spent over fifteen years training and studying in England and Canada. He now holds the role of Honorary Consultant Neurosurgeon at Leeds Teaching Hospitals and Associate Professor at the University of Leeds. Ryan is the first and only academic neurosurgeon at Leeds, a role made possible through funding from Candlelighters and Yorkshire’s Brain Tumour Charity. He co-leads the Stem Cells and Brain Tumour laboratory group with Dr Heiko Wurdak.

By helping to fund his role, Ryan has been able to dedicate time to secure further funding for specific research projects. This is called ‘pump priming’, a method of funding projects at an early stage of development to attract substantial and longer-term national or international funding through grant applications.
Ryan and his colleagues have secured over £2m in funding through grant applications for a wide range of brain cancer research studies.
The grants Ryan has secured are making the following research projects possible at Leeds:
- A study of leftover (margin) cells in brain tumours and testing of new drugs in the tumour cavity.
- Using nanoparticles to selectively target and deliver drugs in gliomas.
- Developing an ultra-precise laser to target leftover cancer cells after surgery.
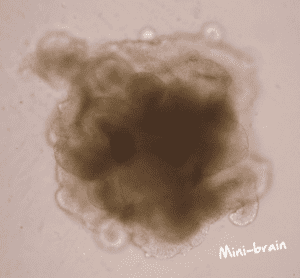
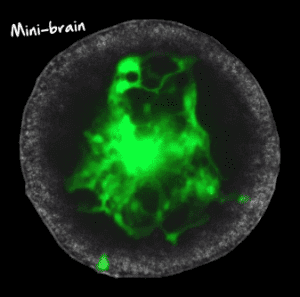
- Understanding glioma invasion and migration using assembloids (so-called ‘mini-brains’).
- Developing a benchtop test for brain cancer to predict patient-specific response to chemotherapy and radiotherapy using ‘mini-brains’.
- PhD to develop artificial intelligence to analyse speech for early detection of brain tumours
- MRes Studentship – Using augmented reality in patient education and Multi-Disciplinary Team working (including brain tumours).
- MRes Studentship – Using augmented reality in neuro-rehabilitation (including brain tumour patients).
- Further studies into anti-epileptics in glioma, seizure prophylaxis in glioma patients and a meningioma study.
Ryan has told us about some of these exciting research projects:
Targeted Drug Delivery and use of Nanoparticles
An exciting new three year project the team are working on alongside colleagues in Nottingham and York is looking at localised drug delivery to target leftover cancer cells. The support of Ryan’s role by Candlelighters has allowed them to obtain a grant of £300k from Brain Research UK to undertake this new research. Ryan tells us, “As surgeons when we operate to get to the tumour we’re right there in the cavity where the leftover cells are. Rather than closing all that up and two weeks down the line trying to give something through a drip that has to get to the same place, could we deliver something at the time of surgery that attacks those leftover cells then and there itself? We don’t really have any agents at the moment that attack cancer in the cavity at the time of surgery.” It is expected that this work will provide a resource that can be used across the UK so that other researchers’ can also trial their own drugs and treatments in the tumour cavity.
Ryan has additionally been part of a team that has secured a £485k three year New Investigator Award from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) to investigate using nanoparticles to selectively target and deliver drugs in gliomas. Ryan says, “Nanoparticles are microscopic objects that can be made from precious metals or structured chemicals. They can be loaded with drugs and then injected into patients. Because they have a ‘lock and key’ mechanism built into them, they will only enter the cells that they are designed to target – in our case, the brain cancer cells. It is important that we don’t get the drug into non-cancerous brain cells. Once the nanoparticles get inside the cells, they can release the drug they are holding, and this can act on the cell.”
Precision Laser Treatment
Targeting leftover cells in the margin zone of a tumour cavity is challenging because they are hard to see and also because they are intermingled with normal brain cells. However, it is essential to get rid of them as they are responsible for the tumour re-growing. Therefore a high-precision device is required that can both ‘see’ and destroy them
Ryan has been part of teams that have secured two grants to enable crucial work into this area. The first is a £1.2m three year grant from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC). This will see Ryan as part of a team working with researchers in Scotland to see if a high-precision laser can be adapted to brain cancer cells and ultimately trialled in surgery to leave fewer cells behind.
A further £30k through Seed Corn Project funding at Heriot-Watt University will allow a six month project to investigate using pulsed laser treatment for brain cancer, to determine the benefits of this method of precision targeting.
Early Predictors of Brain Cancer
The Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare team at Leeds are also looking into potential early predictors of brain cancer as part of a three year PhD using artificial intelligence to analyse speech. Ryan and his co-supervising computer scientist (He Wang) are looking at speech and language and whether there could be an early predictor to trigger a scan in someone with a brain tumour. Ryan explains “a lot of brain tumours tend to grow in areas that are important for speech, memory, thinking and language. The brain is our most eloquent organ, it’s what makes us think and talk. A lot of our patients and their relatives will often say, ‘if I think about it now, maybe six weeks ago, he or she has been a bit odd or did say a couple of odd things’. We had the idea that we can use this to develop an early detection test. This is something that can also be developed to work for children.”
Immersive Technology
In addition to laboratory research, Ryan and his colleagues are also interested in the potential uses of new technologies for cancer treatment. Ryan has been able to secure two MRes studentships for one year, each to look at virtual and augmented reality for patient education and rehabilitation. Ryan explains “we’re looking into being able to generate holograms that children and adults can interact with, which will also aid in understanding the disease. Our trainees spend years understanding the complexities of the brain, so for the general public, to understand where a tumour might be in their head is a very difficult concept. Our idea is that the patient and the doctor will wear a headset to look at an augmented reality hologram of their scan which can be manipulated in space to show them where the tumour is. It’s really cool, I can’t wait. We’re doing the preliminary work for that now to start the actual hands-on work in 2021.”
Ryan has other ambitions for the use of such technologies, and in an article written for The Royal College of Surgeons, he describes a future using immersive technologies to plan or ‘rehearse’ complicated operations in advance, and to play a huge role in the training of future surgeons.
Other Discoveries
The team at Leeds have made many other discoveries already over the last two years since Ryan received funding from Candlelighters. He told us “we’ve also found that cancer cells form networks, so when you hit them with chemotherapy, for example, they’re able to dilute the effect of that chemotherapy by spreading it out amongst themselves. That’s a major challenge for treatment.”
Ryan discovered during his PhD that cancer stem cells don’t form normal mini-brains. Why that is, is being looked at by his team now. “Why are they unable to form normal cells? Well, obviously, because it’s advantageous to them not to because as soon as they form as a normal cell, they’re not cancerous anymore. We’ve found that of the little tumours we grow inside the mini-brains in the lab, the cancer cells are able to do this (form a tumour), but if we use healthy brain cells, they can’t form little tumours. So that’s, again, a really interesting finding that will impact the treatment targets.”
All of these findings by Ryan, Heiko and their team are helping to deepen our understanding of the biology of brain cancers and tumours to work towards better treatments and eventually a cure.
The Impact of COVID-19 on Brain Cancer Research
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a catastrophic effect on all facets of life across the UK and globally, including the research laboratories at Leeds. Ryan told us, “the labs there had to be shut down for six months which meant we weren’t able to do any experiments in the labs. There have been clinical trials we’ve been unable to start and we’ve lost ground on those for nearly a year”. Ryan is also concerned that there will also be a future issue with funding. “Moving forward, all charities are going to have a huge impact on their funding which potentially is going to have a big impact.”
The Impact of Funding from Candlelighters
Ryan tells us, “Quite simply, I wouldn’t exist in this job without the investment of Candlelighters and Yorkshire’s Brain Tumour Charity. If you really want to make progress in things like cancer and brain tumours, you need people who are funded to do that work, who literally have the time paid to be able to run research groups, to be able to bring more funding in, to be able to even just collaborate with other groups around the world or the country. Thankfully, Candlelighters and Yorkshire’s Brain Tumour Charity stepped up and without the investment from both these, this job wouldn’t exist.”
Ryan explains that funding from Candlelighters has allowed him to do much more than just his role and his research. “Another part of what I do is try to build a pipeline of researchers. Because I’ve had the time to invest in this, we now have our first academic junior trainee neurosurgeon starting from August 2021, one of only five in the UK. We’re starting to build a pipeline of academics coming into Leeds. We will combine all aspects of neurosurgical training and academic research into a holistic training scheme which is fundamental to build the next generation of academic neurosurgeons. Without the time the funding Candlelighters and Yorkshire’s Brain Tumour Charity has afforded me, I wouldn’t be able to do any of this. Building a culture, the infrastructure and the institutional idea of academia is really important.”
The work Ryan has done to help secure new roles and over £2m of funding for brain cancer research has meant that the team is about to go through a massive expansion within the next six months, from a team of three to a team of eight. For the UK, a group this size is quite large, and to have this expertise at Leeds dedicated to brain cancer research is incredibly exciting. Candlelighters are very proud to have helped to play a part in this and look forward to the advancements in brain cancer understanding and treatment that will be found.
Candlelighters has a mission to bring hope to families by investing in vital research, education and training. Our aim is to improve the outcomes and lives of children and their families affected by childhood cancer. In the last 20 years alone we have invested over £9m into cancer research but more must be done. Help us to support research like Ryan’s by making a donation, here.
You might also like...






